deepmerge源码 🔗
最近在看webpack-chain源码的时候,看到内部在合并webpack配置的时候使用的是deepmerge这个第三方库,看了一下源码一共一百来行,简单学习一下
https://github.com/TehShrike/deepmerge
使用 🔗
主要功能就是实现两个对象的合并,通key的情况下会进行合并
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| const x = {
foo: { bar: 3 },
array: [{
does: 'work',
too: [ 1, 2, 3 ]
}]
}
const y = {
foo: { baz: 4 },
quux: 5,
array: [{
does: 'work',
too: [ 4, 5, 6 ]
}, {
really: 'yes'
}]
}
const output = {
foo: {
bar: 3,
baz: 4
},
array: [{
does: 'work',
too: [ 1, 2, 3 ]
}, {
does: 'work',
too: [ 4, 5, 6 ]
}, {
really: 'yes'
}],
quux: 5
}
merge(x, y) // => output
|
源码 🔗
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function deepmerge(target, source, options) {
options = options || {}
options.arrayMerge = options.arrayMerge || defaultArrayMerge
options.isMergeableObject = options.isMergeableObject || defaultIsMergeableObject
// cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified is added to `options` so that custom arrayMerge()
// implementations can use it. The caller may not replace it.
options.cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified = cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified
// 源对象和目标对象是否是数组
var sourceIsArray = Array.isArray(source)
var targetIsArray = Array.isArray(target)
// 是否是相同类型
var sourceAndTargetTypesMatch = sourceIsArray === targetIsArray
// 不同类型时
if (!sourceAndTargetTypesMatch) {
return cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified(source, options)
} else if (sourceIsArray) { // 同为数组
return options.arrayMerge(target, source, options)
} else { // 同为非数组对象
return mergeObject(target, source, options)
}
}
|
cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified 🔗
是否克隆出一个新对象,默认行为是进行克隆, 最终还是都的deepmerge主函数
1
2
3
4
5
| function cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified(value, options) {
return (options.clone !== false && options.isMergeableObject(value))
? deepmerge(emptyTarget(value), value, options)
: value
}
|
defaultArrayMerge 🔗
默认同为数组时进行合并的逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
| function defaultArrayMerge(target, source, options) {
return target.concat(source).map(function(element) {
return cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified(element, options)
})
}
|
利用数组concat返回一个新元素的情况,并且遍历数组元素进行创建新元素
mergeObject 🔗
合并对象的主逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| function mergeObject(target, source, options) {
var destination = {}
if (options.isMergeableObject(target)) {
getKeys(target).forEach(function(key) {
destination[key] = cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified(target[key], options)
})
}
getKeys(source).forEach(function(key) {
if (propertyIsUnsafe(target, key)) {
return
}
if (propertyIsOnObject(target, key) && options.isMergeableObject(source[key])) {
destination[key] = getMergeFunction(key, options)(target[key], source[key], options)
} else {
destination[key] = cloneUnlessOtherwiseSpecified(source[key], options)
}
})
return destination
}
|
其中getKeys实现比较有意思
1
| Object.keys(target).concat(getEnumerableOwnPropertySymbols(target))
|
首先使用Object.keys获取到对象可枚举属性组成的数组
再使用Object.getOwnPropertySymbols拿到对象上所有Symbol属性的数组
这里就比较严谨了,兼融了对象上的可以访问的属性
- 创建一个新的空对象
- 遍历目标对象,把目标对象上的属性进行复制
- 遍历源对象
- 如果目标对象上有对应的同属性,进行复制合并
- 没有的话进行创建新的值
笔记 🔗
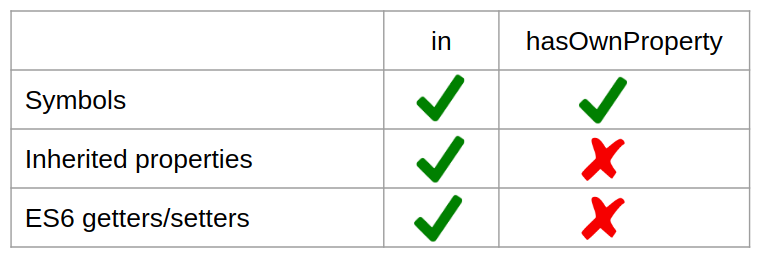
in和hasOwnProperty区别- 都可以用来对象内是否含有对应属性
- 都支持判断ES6内的
symbols - 不同点就是
in可以判断出原型链上通过继承过来的属性, hasOwnProperty只能判断对象上自己拥有的属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| const obj = { answer: 42 };
// 基础属性判断
'answer' in obj; // true
obj.hasOwnProperty('answer'); // true
'does not exist' in obj; // false
obj.hasOwnProperty('does not exist'); // false
// symbol对象判断
const symbol = Symbol('answer');
const obj = { [symbol]: 42 };
symbol in obj; // true
obj.hasOwnProperty(symbol); // true
// 继承属性判断
'constructor' in obj; // true
'__proto__' in obj; // true
'hasOwnProperty' in obj; // true
obj.hasOwnProperty('constructor'); // false
obj.hasOwnProperty('__proto__'); // false
obj.hasOwnProperty('hasOwnProperty'); // false
class BaseClass {
get baseProp() {
return 42;
}
}
class ChildClass extends BaseClass {
get childProp() {
return 42;
}
}
const base = new BaseClass();
const child = new ChildClass();
// 对于es6中 getters/setters判断
'baseProp' in base; // true
'childProp' in child; // true
'baseProp' in child; // true
base.hasOwnProperty('baseProp'); // false
child.hasOwnProperty('childProp'); // false
child.hasOwnProperty('baseProp'); // false
|